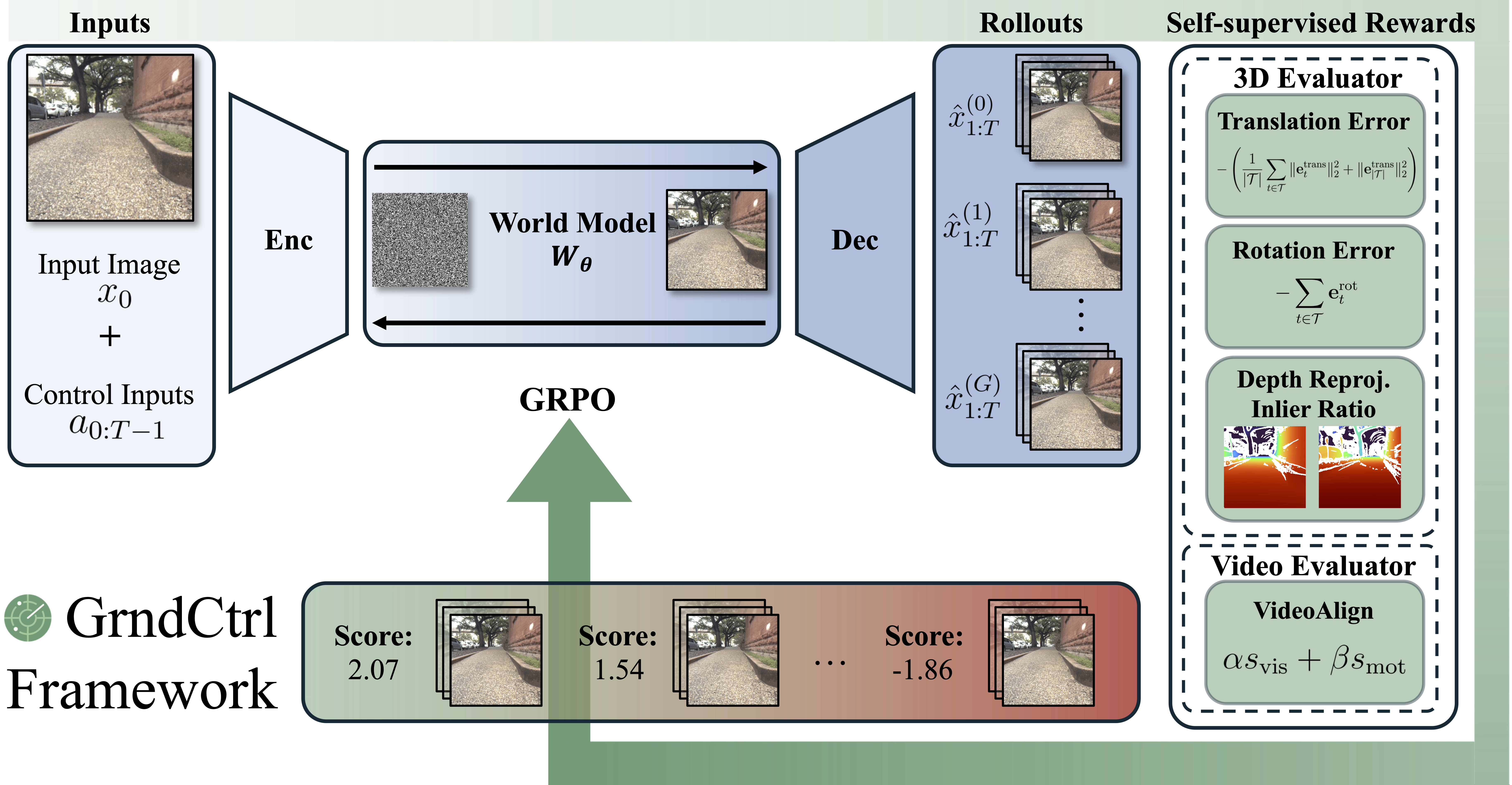
Overview
Reinforcement Learning with World Grounding (RLWG) addresses geometric inconsistencies in pretrained video world models through self-supervised post-training with verifiable rewards. Instead of reconstruction losses, RLWG grounds models using geometric and perceptual rewards from frozen evaluators.
GrndCtrl instantiates RLWG using Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), enabling physically consistent rollouts essential for reliable world generation.